February 28, 2024
2 minutes reading
Simultaneous order generation is essential for active investors, especially those handling large funds, as it allows multiple trade orders to be executed simultaneously, thereby maximizing trading opportunities and managing risk more effectively. The key to achieving this synchronization in Python is to use it ThreadPoolExecutor from concurrent.futures section, as shown in the provided sample code.
This approach allows traders to send multiple orders in parallel, significantly reducing the time required to execute trades and allowing for a more efficient management of trading strategies. Below, we’ll go through a short tutorial on how to place concurrent orders using Python, leveraging the ThreadPoolExecutor to achieve effective identification.
What is ThreadPoolExecuteor?
ThreadPoolExecutor is a high-level interface for asynchronous execution of callees, provided by the concurrent.futures module in Python. It removes the management of a thread pool, allowing you to run tasks concurrently, thereby improving the performance of I/O-bound and high-latency activities. This executor is particularly useful in scenarios where running operations in parallel can significantly reduce the overall execution time, such as making multiple network requests, performing I/O operations, or handling computational tasks that can be distributed across multiple threads.
import requests
import time
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
# Define the URL and the JSON payload
url = 'http://127.0.0.1:5000/api/v1/placeorder'
data = {
"apikey": "<apikey>",
"strategy": "Test Strategy",
"symbol": "NIFTY29FEB2422100CE",
"action": "BUY",
"exchange": "NFO",
"pricetype": "MARKET",
"product": "NRML",
"quantity": "1000"
}
# Function to send a POST request
def send_order(data):
start_time = time.time()
response = requests.post(url, json=data)
end_time = time.time()
response_time_ms = (end_time - start_time) * 1000
return f"API Order Response Time: {response_time_ms:.2f} milli seconds"
# Start measuring total time
total_start_time = time.time()
# Use ThreadPoolExecutor to send requests in parallel
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=5) as executor:
# Create a list to hold references to the future objects returned by submit
futures = [executor.submit(send_order, data) for _ in range(10)]
# Iterate through the future objects to get the results
for count, future in enumerate(futures):
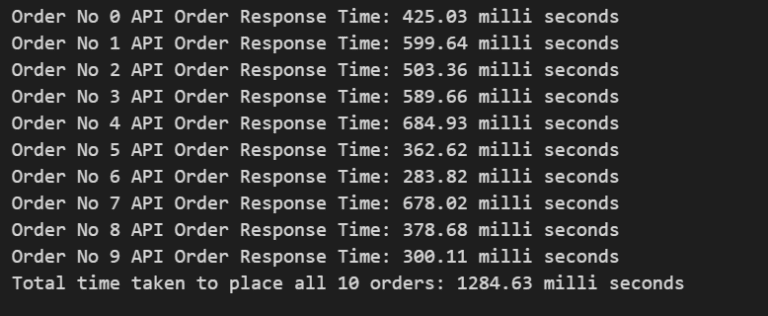
response_time = future.result()
print(f"Order No {count} {response_time}")
# Stop measuring total time
total_end_time = time.time()
total_time_ms = (total_end_time - total_start_time) * 1000
print(f"Total time taken to place all 10 orders: {total_time_ms:.2f} milli seconds")
Production

Understand Setup
Before diving into simultaneity, it’s important to understand the setup. The provided sample code uses the requests library for sending HTTP POST requests to a transaction API and the concurrent.futures module to achieve concurrent use. The target API endpoint is a dummy URL (http://127.0.0.1:5000/api/v1/placeorder), and the data payload includes details such as API key, trading strategy, symbol, action, exchange, price type, product and quantity.
Specify the order shipping mode
The send_order the function takes a data dictionary as input, representing the details of the order. Sends a POST request to the API endpoint and measures the response time, returning a string containing the API order response time in milliseconds. This function is necessary to encapsulate the logic required to send a single order to the trading platform.
Implement concurrency with ThreadPoolExecutor
The real power of sample code is in its use ThreadPoolExecutor from concurrent.futures unit to ship orders at once. The ThreadPoolExecutor is initialized with a max_workers parameter, which specifies the number of threads to use for dispatching orders. In the example, max_workers=5 means that five orders can be shipped at the same time.
Sending Simultaneous Orders
Inside ThreadPoolExecutor management environment, futures contracts are created to send orders at the same time. A future represents an asynchronous execution that can be requested for the state or result without blocking the calling thread. With the call executor.submit(send_order, data) for each order, the code schedules the send_order operation to be performed simultaneously for each order. The submit method returns a future object, which is stored in a list (futures).
After placing the orders, the code is repeated above futures list, calling future.result() in every. This call blocks until the order response is received, allowing collection of response times for each order.
Measure the total execution time
The total execution time for placing all orders is measured by recording the start and end times before and after the concurrent execution block. This shows the efficiency gained by using simultaneous orders instead of sending them sequentially.
Using ThreadPoolExecutor for placing orders simultaneously, active traders can significantly reduce the time required to execute multiple orders. This approach is especially beneficial when it comes to large funds, where the speed of order execution can affect the success of the overall trading strategy. The provided sample code demonstrates a simple method for implementing concurrent commands, emphasizing the importance of concurrency in active transaction environments.